How To Install Apache Tomcat In Centos 6
Apache Tomcat is an open-source web server and servlet container developed by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF).
Tomcat implements the Java Servlet and the JavaServer Pages (JSP) specifications from Oracle and provides a "pure Java" HTTP web server surroundings for running the Java codes.
Apache Tomcat includes tools for configuration and management, but can likewise be configured by editing XML configuration files.
Hither is the step past step guide to install Apache Tomcat 9.0 / 8.5 on CentOS 6 / RHEL half dozen.
Prerequisites
Install Java
Tomcat requires to accept a stable release of Java 8 or afterward installed on your machine. You tin either install Oracle JDK or OpenJDK on your machine.
Here I will use OpenJDK.
yum install -y java-1.eight.0 wget
Y'all can also verify Java by issuing the following command.
java -version
Output:
openjdk version "ane.8.0_222" OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build one.8.0_222-b10) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.222-b10, mixed mode)
Create a Service Account
For best practise, Tomcat should never be run equally a privileged user (root). So, create a low-privilege user for running the Tomcat service.
useradd -d /opt/tomcat tomcat
Install Apache Tomcat
Download Apache Tomcat
Download Apache Tomcat from the official website.
### Apache Tomcat nine.0 ### wget https://www-us.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-nine/v9.0.22/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.22.tar.gz ### Apache Tomcat viii.5 ### wget https://www-us.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-eight/v8.5.43/bin/apache-tomcat-8.5.43.tar.gz
Setup Apache Tomcat
Extract the tomcat on to your desired (/opt/tomcat) directory.
tar -zxvf apache-tomcat-*.tar.gz mv apache-tomcat-*/* /opt/tomcat/ chown -R tomcat:tomcat /opt/tomcat/
Create Init Script
Apache Tomcat can be started and stopped manually by the script which comes with the bundle. But, here, we will utilise the init script to handle information technology.
vi /etc/init.d/tomcat9
Use the beneath information.
#!/bin/bash # chkconfig: 2345 95 xx # description: This application was adult by me and is tested on this server # processname: my_app # # Tomcat 8 start/finish/status init.d script # Initially forked from: https://gist.github.com/valotas/1000094 # @author: Miglen Evlogiev <fustigate@miglen.com> # # Release updates: # Updated method for gathering pid of the current proccess # Added usage of CATALINA_BASE # Added coloring and additional status # Added check for existence of the tomcat user # Added termination proccess #Location of JAVA_HOME (bin files) export JAVA_HOME= /usr/lib/jvm/jre-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64/ #Add Java binary files to PATH export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH #CATALINA_HOME is the location of the bin files of Tomcat export CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat/ #CATALINA_BASE is the location of the configuration files of this instance of Tomcat export CATALINA_BASE= /opt/tomcat/ #TOMCAT_USER is the default user of tomcat consign TOMCAT_USER=tomcat #TOMCAT_USAGE is the message if this script is chosen without any options TOMCAT_USAGE="Usage: $0 {\eastward[00;32mstart\e[00m|\east[00;31mstop\e[00m|\e[00;31mkill\e[00m|\e[00;32mstatus\e[00m|\e[00;31mrestart\e[00m}" #SHUTDOWN_WAIT is wait time in seconds for java proccess to finish SHUTDOWN_WAIT=20 tomcat_pid() { echo `ps -atomic number 26 | grep $CATALINA_BASE | grep -v grep | tr -due south " "|cut -d" " -f2` } kickoff() { pid=$(tomcat_pid) if [ -n "$pid" ] and then repeat -e "\due east[00;31mTomcat is already running (pid: $pid)\e[00m" else # Beginning tomcat echo -e "\e[00;32mStarting tomcat\e[00m" #ulimit -n 100000 #umask 007 #/bin/su -p -s /bin/sh $TOMCAT_USER if [ `user_exists $TOMCAT_USER` = "1" ] so /bin/su $TOMCAT_USER -c $CATALINA_HOME/bin/startup.sh else sh $CATALINA_HOME/bin/startup.sh fi status fi render 0 } condition(){ pid=$(tomcat_pid) if [ -n "$pid" ]; then repeat -eastward "\e[00;32mTomcat is running with pid: $pid\e[00m" else repeat -e "\e[00;31mTomcat is not running\due east[00m" fi } terminate() { echo -e "\eastward[00;31mTerminating Tomcat\due east[00m" impale -nine $(tomcat_pid) } stop() { pid=$(tomcat_pid) if [ -n "$pid" ] and so echo -e "\e[00;31mStoping Tomcat\eastward[00m" #/bin/su -p -due south /bin/sh $TOMCAT_USER sh $CATALINA_HOME/bin/shutdown.sh let kwait=$SHUTDOWN_WAIT count=0; until [ `ps -p $pid | grep -c $pid` = '0' ] || [ $count -gt $kwait ] do repeat -n -east "\n\e[00;31mwaiting for processes to leave\e[00m"; slumber 1 let count=$count+1; done if [ $count -gt $kwait ]; and so echo -north -e "\n\e[00;31mkilling processes didn't finish after $SHUTDOWN_WAIT seconds\e[00m" end fi else repeat -e "\e[00;31mTomcat is non running\e[00m" fi return 0 } user_exists(){ if id -u $i >/dev/null 2>&ane; then repeat "1" else repeat "0" fi } instance $one in first) beginning ;; terminate) finish ;; restart) stop start ;; status) status ;; impale) terminate ;; *) echo -e $TOMCAT_USAGE ;; esac exit 0
Credit: Timothy Hutz.
Set up the script to exist executable.
chmod +x /etc/init.d/tomcat9
Start Apache Tomcat
Commencement the service.
service tomcat9 beginning
Y'all can verify the service running, by default tomcat runs on port no 8080
netstat -antup | grep 8080
Output:
tcp 0 0 :::8080 :::* Listen 1526/java
Enable the Tomcat service to start automatically on system startup.
chkconfig --add together tomcat9 chkconfig tomcat9 on
Firewall
Allow Tomcat spider web awarding requests through the firewall.
iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 8080 -j Have /etc/init.d/iptables salvage
Configure Apache Tomcat Web UI
Tomcat can be managed through the web-manager and virtual host manager. Both Web manager and Host manager are password protected and require username and password to access.
The user with manager-gui and admin-gui function take access to spider web awarding manager and host-manager, respectively. These users and roles are defined in tomcat-users.xml.
vi /opt/tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml
Place the following two lines just above the last line.
<role rolename=" admin-gui,manager-gui "/> <user username=" admin " countersign=" tomcat " roles="manager-gui,admin-gui"/>
For security reason, Spider web Director and Host Manager are accessible only from the localhost, i.east., from the server itself.
To access spider web and host managers from the remote arrangement, you lot would demand to add your source network in the let list. To do that, edit the beneath two files.
### Web Managing director ### vi /opt/tomcat/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml ### Host Manager ### vi /opt/tomcat/webapps/host-managing director/META-INF/context.xml
Update the beneath line on above files with source IP from which your accessing the web and host Manager. .* will allow anybody to take access to both managers.
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::i|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 |.* " /> OR
You can as well allow part of your network only. For case: To allow the 192.168.one.0/24 network only, you can use the below values.
permit="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::ane|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 |192.168.1.* " /> Restart the Tomcat service.
service tomcat9 restart
Access Apache Tomcat
Open up the web browser and point to
http://ip.add.re.ss:8080
You lot would get the Tomcat default page.
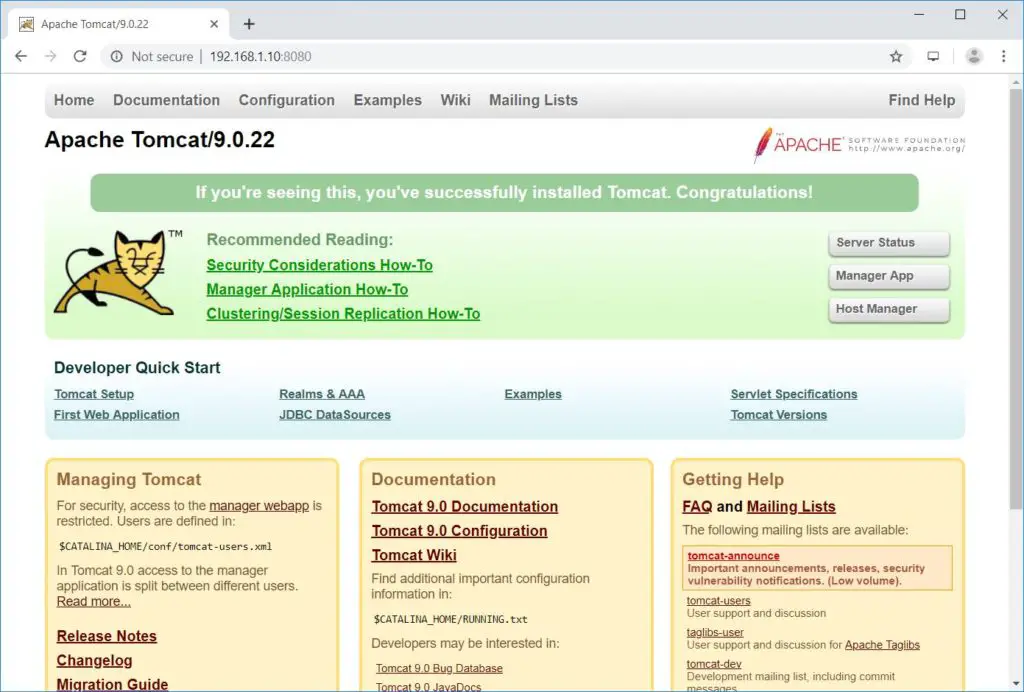
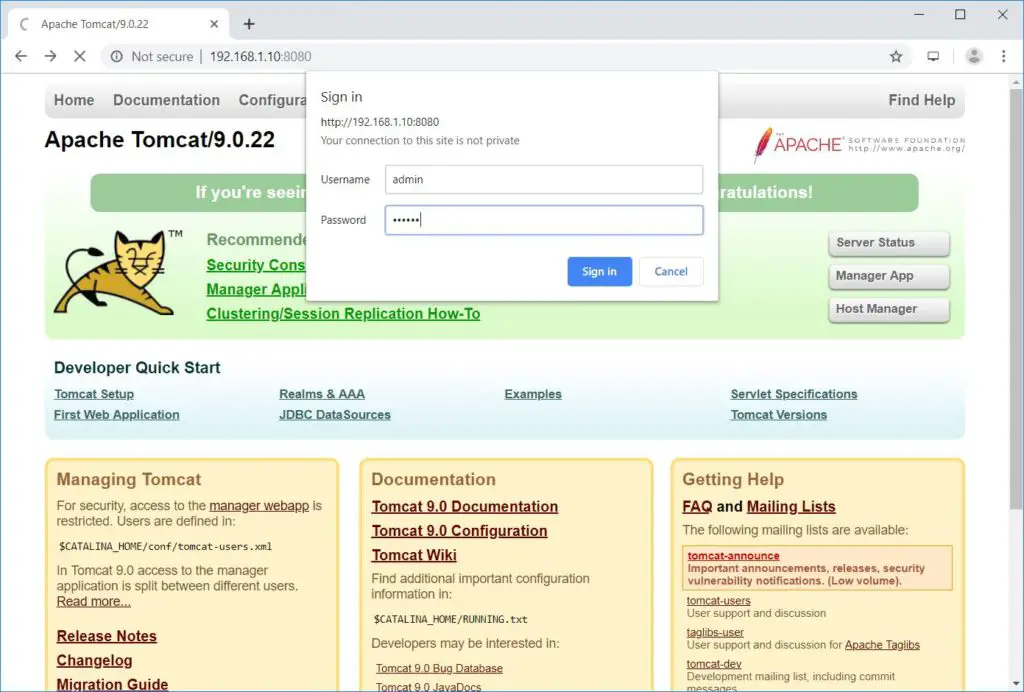
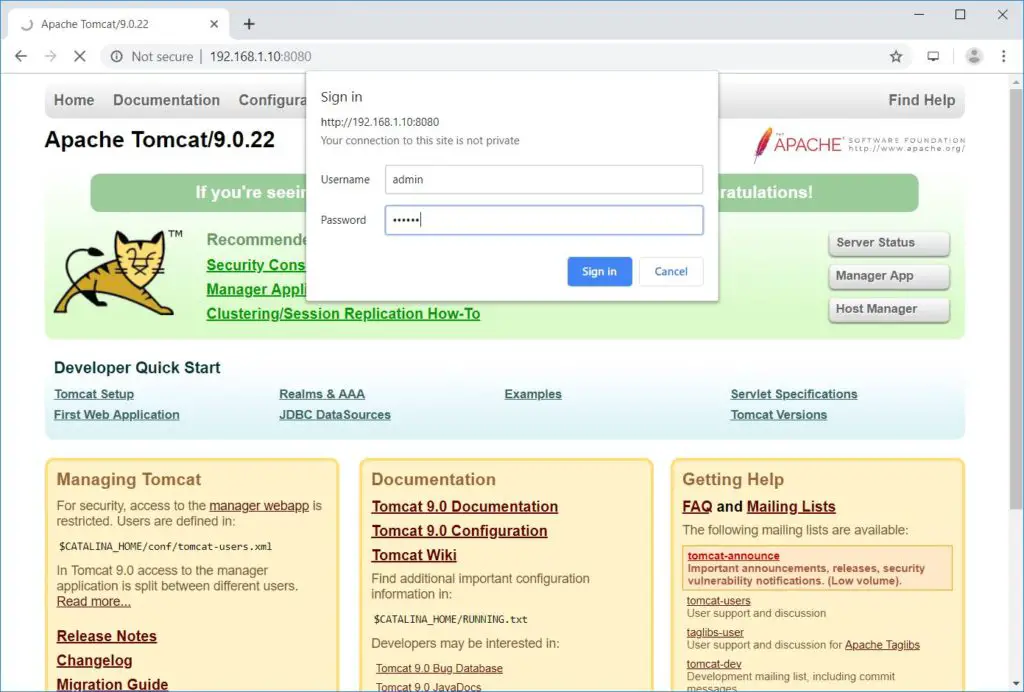
Web Manager: – Login Required. Username: admin, Countersign: tomcat.
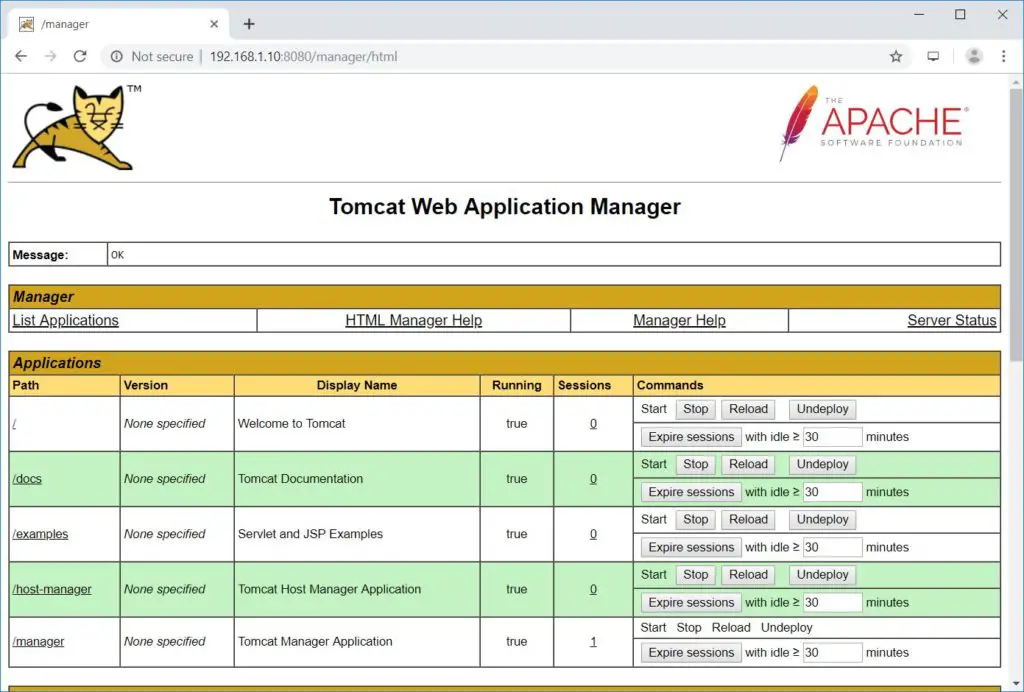
Here, you can deploy a new awarding, deploy a new application on specified context, list the active or inactive applications, start and stop the spider web applications.
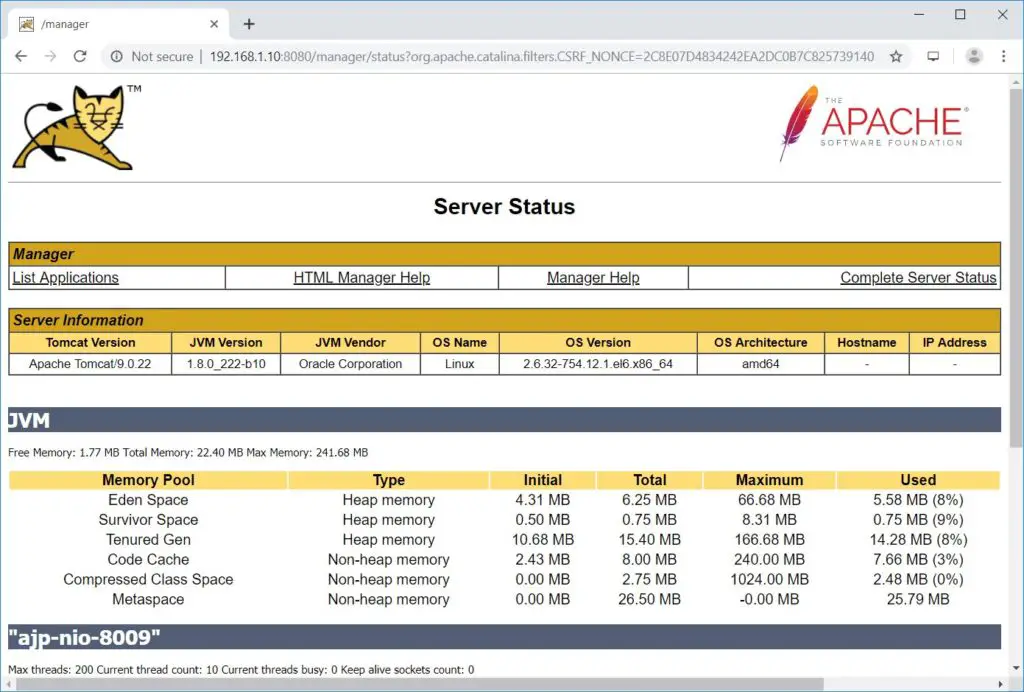
Also, you can check the server status.
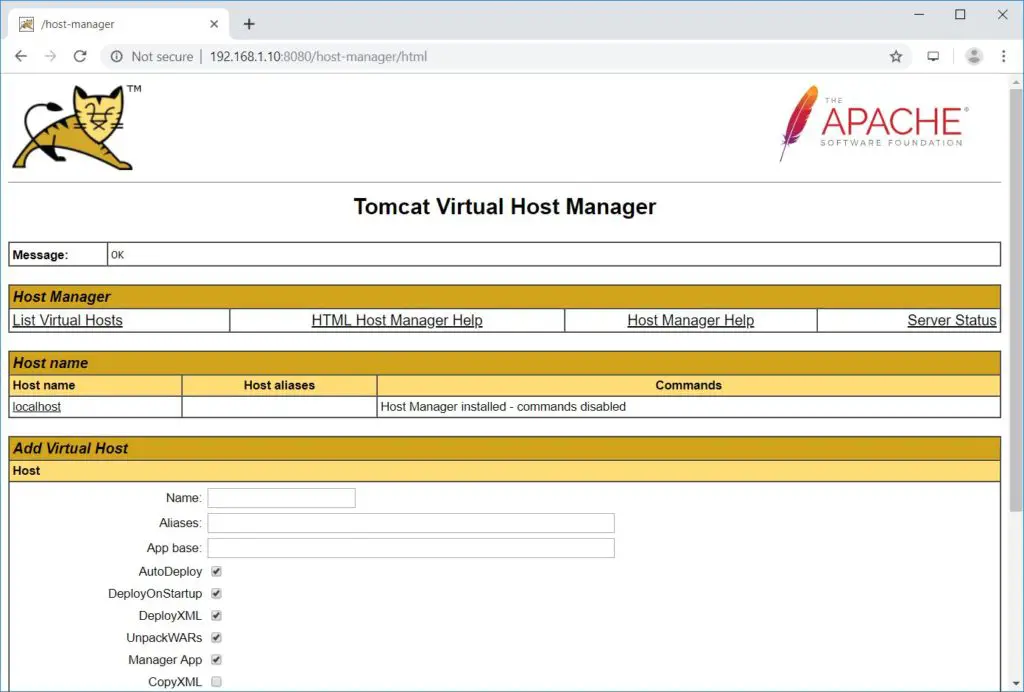
Host Manager: – Login Required. Username: admin, Password: tomcat.
Here, you can handle virtual hosts of Tomcat.
Decision
That'southward All. I promise you lot have learned how to install Tomcat nine on CentOS 6 / RHEL 6. You are at present ready to deploy your first web application. As a security recommendation, consider implementing SSL/TLS for Tomcat
Source: https://www.itzgeek.com/how-tos/linux/centos-how-tos/install-apache-tomcat-7-0-on-rhel-6-centos-6.html
Posted by: turnagethadfice.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Install Apache Tomcat In Centos 6"
Post a Comment